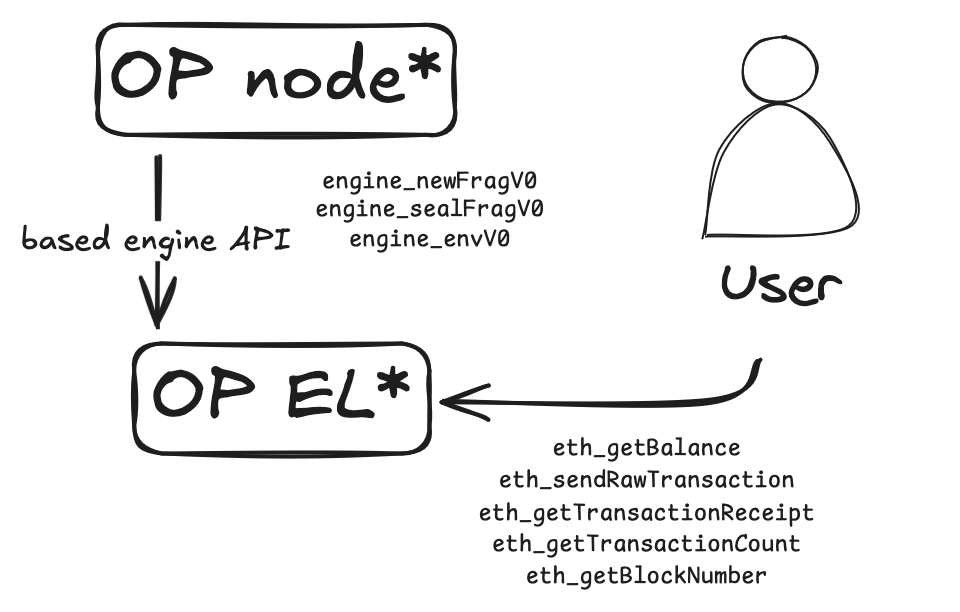
Execution
The OP geth was upgraded to receive Frags messages from the OP node, as well as to serve state for RPC calls off the "unsealed block".
Because Frags are shared continously from the gateway, the EL can already start pre-processing and preparing for the block seal and sync.
The forked repo with changes can be found in based-op-geth.
Unsealed Block
We define a new structure, UnsealedBlock that represents a block being reconstructed locally from Frags.
type UnsealedBlock struct {
Env *Env
Frags []Frag
LastSequenceNumber *uint64
Hash common.Hash
Receipts Receipts
}
Starting a new unsealed block
After an engine_envV0 call is received, the EL initializes a new unsealed blocks and prepares the block environment for frags to be applied.
For the message to be valid, the following conditions must be met:
- There must not be a an unsealed block in progress.
- The timestamp must be greater than the previous block's timestamp.
- The block number must be the next one in the sequence.
- The parent hash must match the previous block's hash.
After validation, the unsealed block is persisted in the global state via SetCurrentUnsealedBlock.
Inserting frags
Upon receiving engine_newFragV0 calls, the EL validates the received frag:
- The block number must match the current unsealed block number and there must be an opened unsealed block.
- The sequence number must be the next one in the sequence (the current unsealed block persists this number). This has several cases:
- Before checking the sequence number is the correct one, we must make sure that the current unsealed block's last frags was not the final one (meaning this block is treated as sealed).
- If the sequence number is 0 and the unsealed block did not received the last frag, then the frag is the first one and the current unsealed block must have the
LastSequenceNumberset to nil. - If the sequence number is > 0 and the unsealed block did not received the last frag, then the frag should be the next in the sequence.
If valid, the frags are added to the unsealed block. This means executing every transaction in the frag and adding the receipts to the unsealed block.
If the frag is marked as last, the node starts sealing the block and computing the state root.
Seal verification
With the engine_sealFragV0 call, the node verifies that the sealed block matches with what the gateway computed. If the verification is successful, the node sets the block as canonical and advances the chain.